Side-boat tow to test the influence of flaps in a 2-meter planing craft model
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.25043/19098642.70Keywords:
planing boat, model testAbstract
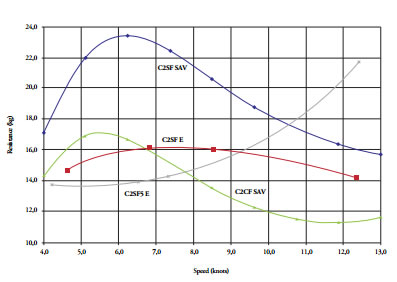
A small craft is considered in the planing regime when its Froude number is higher than 1.2, and under that condition its weight is mainly supported by hydrodynamic pressure acting on the bottom of the hull. It is also known that installing stern flaps at a certain angle from the bottom line will alter the trim angle and, as a consequence, the resistance exerted by the water. In this work, using the classical work from Savitsky, the resistance on a planing craft is estimated, including the effect of flaps, and then the influence of those appendages on the hydrodynamic behavior of a craft of local design was experimentally verified. The wooden model was 2.0 meters long and was side towed from an outboard powered boat, with a 3.2-m arm, in a small artificial lake. The tests were run between 5 and 12 knots, with uneven intervals due to the outboard control; the model was towed without and with flaps at 5 and 10°. Finally, experimental and empirical results for towing force and trim angle were plotted. In some of the experimental curves the presence of humps may be identified, but less pronounced than with the theoretical results. Experimental resistance values are lower than those obtained from Savistky’s formulation for no flaps; in the case of flaps at 5°, the agreement in trim angle was very good. Finally, the benefit of flaps on the performance of the planing model was corroborated, but it should be emphasized that this improvement is only valid for a certain velocity range.
Downloads
References
BENITES, D. A., Pruebas Experimentales para Determinar la Influencia de Flaps en la Resistencia al Avance de una Lancha Planeadora de 11 metros, Naval Engineer Thesis, Faculty of Maritime Engineering, ESPOL, Guayaquil, Ecuador, 2012.
BROWN, W. AND SAVITSKY, D., Procedures for Hydrodynamic Evaluation of Planing Hulls in Smooth and Rough Water, Marine Technology, SNAME, Vol 13, No.4, 1976.
FALTINSEN, O., Hydrodynamics of High-Speed Marine Vehicles, Cambridge University, 2005.
ITTC, Recommended Procedures and Guidelines – Testing and Extrapolation Methods (Resistance Test for High Speed Marine Vehicles), 7.5-02-05-01, 2002.
SAVITSKY, D., Hydrodynamic Design of Planing Hulls, Marine Technology, SNAME, Vol. I, 1964.
VAN MANEN, Resistance, Ch. 5 in Principles of Naval Architecture Vol II, E. Lewis, Ed., SNAME, 1988.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
The authors who publish in this Journal certify that:
- The work submitted for publication in The Ship Science and Technology journal, was written by the author, given that its content is the product of his/her direct intellectual contribution.
- All data and references to material already published are duly identified with their respective credits and are included in the bibliographic notes and quotations highlighted as such.
- All materials submitted for publication are completely free of copyrights; consequently, the author accepts responsibility for any lawsuit or claim related with Intellectual Property Rights thereof, Exonerating of responsibility to The Science and Technology for the Development of Naval, Maritime, and Riverine Industry Corporation, COTECMAR.
- In the event that the article is chosen for publication by The Ship Science and Technology journal, the author state that he/she totally transfers reproduction rights of such to The Science and Technology for the Development of Naval, Maritime, and Riverine Industry Corporation, COTECMAR.
- The authors retain the copyright and transfer to COTECMAR the right of publication and reproduction of the work which will be simultaneously subject to the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC -BY) , which allows the license to copy, distribute, display and represent the work and to make derivative works as long as it recognizes and cites the work in the manner specified by the author or licensor.
- For more information about the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC -BY) and his use and scope, please visit the following web page https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/legalcode