Electric arc spray coatings for the naval industry
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.25043/19098642.44Keywords:
electric arc spray, abrasive wear, thermal barrier, corrosionAbstract
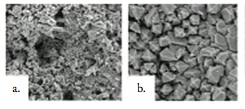
Carbon and stainless steel, as well as Fe-Nb-Cr-W coatings were deposited on steel substrates by using electric arc spray, and its possibility of applying such coatings in the naval industry was analyzed. In order to achieve this, the coating microstructure was characterized before and after the corrosion, abrasive wear, and thermal barrier tests. Corrosion resistance was analyzed via potenciodynamic polarization test using a NaCl electrolyte at 3%; abrasive wear resistance was measured by using a three-component system following ASTM G-65 recommendations, while quality control as thermal barriers was studied by using EIS tests. Scanning Electron Microscopy, optical microscopy and X-ray diffraction were used to characterize the microstructure of the coatings.Downloads
References
LASHRERAS E., MARÍA J. (1978). "Tecnología del acero". Ediciones Cedel. Tercera edición, Barcelona. España.
GEDZEVICIUS I., VALIULIS A. (2006). "Analysis of wire arc spraying process variables on coatings properties". Journal of Materials Processing Technology.
Handbook of Hard Coatings. Tomo 3. Thermal Spraying and Detonation Gun Processes. (2003).
MARULANDA, J. (2000). "El Rociado Térmico y sus Aplicaciones". Publicación Universitaria.
DOBLER K. (2006). "Reconditioning Power Generation Components with Thermal Spray Welding Journal".
Department of the Army. U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Thermal spraying: New construction and Maintenance. EM 1110-2- 3401. Washington, DC 20314-1000. (2005).
COOKE K., OLIVER G., BUCHANAN V., PALMER N. (2007). "Optimisation of the electric wire arc-spraying process for improved wear resistance of sugar mill roller shells". Surface & Coatings Technology 202 185–188.
ASTM Designation: G65. Standard Test Method for Measuring Abrasion Using the Dry Sand/Rubber Wheel Apparatus. (2001).
ASTM G5 – 94. Standard Reference Test Method for Making Potentiostatic and Potentiodynamic Anodic Polarization Measurements. (2004).
GARCÍA J., SALAZAR A., MÚNEZ C.J., UTRILLA V. y POZA P. (2005). “Análisis de la degradación de recubrimientos de barrera térmica por espectroscopía de impedancia electroquímica”. Revista Cerámica y Vidrio, 232-239.
GEORGIEVA, THORPE P., YANSKI R., SEAL A. (2006). “Nanocomposite materials: an innovative turnover for the wire arc spraying technology”. University of Central Florida, Mechanical, Materials and Aerospace Engineering Department.
KRAUSS G. (1989). "Heat Treatment and Processing Principles". Eds, ASM International.
SMITH W. (1993). "Structure and Properties of Engineering Alloys". Mc Graw Hill International Editions.
JANDIN G., LIAO H., FENG Z.Q., CODDET C. (2003). "Correlations between operating conditions, microstructure and mechanical properties of twin wire arc sprayed steel coatings". Materials Science and Engineering A349 298/305.
ZHOU Z., WANG L., WANG F., LIU Y. (2009). “Formation and corrosion behavior of Fe-based amorphous metallic coatings prepared by detonation gun spraying”. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China. S634-s638.
ASM Handbook, Volume 1, Properties and Selection: Irons, Steels, and High Performance Alloys. (2005).
ABEDINI A., POURMOUSA A., CHANDRA S., MOSTAGHIMI J. (2006). “Effect of substrate temperature on the properties of coatings and splats deposited by wire arc spraying”. Surface & Coatings Technology 201 3350–3358.
SONGA S.-H., XIAO P., WENG L.-Q. (2005). “Evaluation of microstructural evolution in thermal barrier coatings during thermal cycling using impedance spectroscopy”. Journal of the European Ceramic Society 1167–1173. 25.
CULHAA O., TOPARLIA M., SAHINB S., AKSOYA T.. (2008). "Characterization and determination of FexB layers mechanical properties”. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 206 231–240.
JIN G., XU B.S, WANG H. D, LI Q. F, WEI S.C. (2007). "Microstructure and tribological properties of stainless steel coatings sprayed by two methods based on spraying". Surface & Coatings Technology 201 5261–5263.
AMOKRANE M., BOUNARB N., BENABBASB A., ATIA A. (2008). “Study of microstructure, phases and microhardness of metallic coatings deposited by flame thermal spray”. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 200 410–415.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
The authors who publish in this Journal certify that:
- The work submitted for publication in The Ship Science and Technology journal, was written by the author, given that its content is the product of his/her direct intellectual contribution.
- All data and references to material already published are duly identified with their respective credits and are included in the bibliographic notes and quotations highlighted as such.
- All materials submitted for publication are completely free of copyrights; consequently, the author accepts responsibility for any lawsuit or claim related with Intellectual Property Rights thereof, Exonerating of responsibility to The Science and Technology for the Development of Naval, Maritime, and Riverine Industry Corporation, COTECMAR.
- In the event that the article is chosen for publication by The Ship Science and Technology journal, the author state that he/she totally transfers reproduction rights of such to The Science and Technology for the Development of Naval, Maritime, and Riverine Industry Corporation, COTECMAR.
- The authors retain the copyright and transfer to COTECMAR the right of publication and reproduction of the work which will be simultaneously subject to the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC -BY) , which allows the license to copy, distribute, display and represent the work and to make derivative works as long as it recognizes and cites the work in the manner specified by the author or licensor.
- For more information about the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC -BY) and his use and scope, please visit the following web page https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/legalcode