Efectos de la distancia interanódica y la geometría del cátodo, en la efectividad de los sistemas de protección catódica por ánodos de sacrificio en embarcaciones
Keywords:
cathodic protection, anodic distribution, olarization, cathode, anodeAbstract
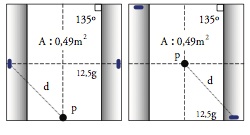
The present article relates determined results derived from the lab study, whose principal objective lies on determining the incidence of the distance between the anodes and the cathode geometry in the life cycle of cathodic protection systems. These investigations are headed towards generating the basic knowledge of the performance of the galvanic cathodic protection systems for ships, with the objective of supporting a software that takes into consideration the influence of all the variables and the current considerations of design.The results prove that the life cycle of the cathodic protection system by sacrifice anodes largely depends on the inter anodic distance adopted in the routine of design and that there is an optimum distance which objectively orients the decision making at the moment of anode assembly on the hull of the ship. Likewise, the geometry of the substrate affects on the life cycle of the system and is interpretable as an amplifying factor of the exposed area which will be protected.
Downloads
References
American Society for Test and Materials (1998), “ASTM D-1141 Standard Practice for the Preparation of Substitute Ocean Water”. ASTM, International Publication.
American Society for Test and Materials (2006), “ASTM B 418 Type II Alloy Standard: Standard Specification for Cast and Wrought GalFuente vanic Zinc Anodes”, ASTM, International Publication.
Corporación para la Investigación de la Corrosión y Corporación de Ciencia y Tecnología para el Desarrollo Naval, Marítimo y Fluvial (2006). Proyecto de investigación “Optimización del sistema de protección catódica por ánodos de sacrificio para embarcaciones de hasta 3.600 toneladas que operan en la bahía de Cartagena”,
Piedecuesta, CIC.
Corporación para la Investigación de la Corrosión y Corporación de Ciencia y Tecnología para el Desarrollo Naval, Marítimo y Fluvial (2006). Proyecto de cofinanciación Colciencias: “Desarrollo de una herramienta computacional que permita predecir y simular el nivel de protección contra la corrosión en embarcaciones marítimas de hasta 3.600 toneladas, las cuales usan sistemas de protección catódica por ánodos de sacrificio”, Piedecuesta, CIC.
Det Norske Veritas (1993), “DNV RP B401 Cathodic Protection Design”, DNV, Oslo.
Military Specification (Revision K) MIL-A-18001 “Anodes, Sacrificial Zinc Alloy”, MIL, International Publication.
Military Specification (1992), MIL-A-24779 (SH) “Detail Specification Anodes, Sacrificial Aluminum Alloy”. MIL, International Publication.
Downloads
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
The authors who publish in this Journal certify that:
- The work submitted for publication in The Ship Science and Technology journal, was written by the author, given that its content is the product of his/her direct intellectual contribution.
- All data and references to material already published are duly identified with their respective credits and are included in the bibliographic notes and quotations highlighted as such.
- All materials submitted for publication are completely free of copyrights; consequently, the author accepts responsibility for any lawsuit or claim related with Intellectual Property Rights thereof, Exonerating of responsibility to The Science and Technology for the Development of Naval, Maritime, and Riverine Industry Corporation, COTECMAR.
- In the event that the article is chosen for publication by The Ship Science and Technology journal, the author state that he/she totally transfers reproduction rights of such to The Science and Technology for the Development of Naval, Maritime, and Riverine Industry Corporation, COTECMAR.
- The authors retain the copyright and transfer to COTECMAR the right of publication and reproduction of the work which will be simultaneously subject to the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC -BY) , which allows the license to copy, distribute, display and represent the work and to make derivative works as long as it recognizes and cites the work in the manner specified by the author or licensor.
- For more information about the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC -BY) and his use and scope, please visit the following web page https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/legalcode